RESEARCH & ANALYSIS


Research and analyse the core characteristics, ethics and theory of design entrepreneurship.
What Is Design Entrepreneurship?
A designer provides a service to a client. They are the trained agents, working at the will of someone else's vision. Design entrepreneurship evades the traditional economic rituals whereby a designer waits for a client to bring them a design problem. Instead, the designers define the problem themselves and develop a solution in a business venture. The answer can often be as creative as its team, price and distribution (What are design entrepreneurship? 2021).
Design isn't just a service industry but a cross-functional way of thinking that is invaluable in starting innovative companies. Thinking like a designer means being better suited for the open-ended ambiguous problems that epitomise the start-up journey and having the skills needed to iterate towards product-market fit (Consultores, 2021).
Both designers and entrepreneurs are problem solvers. Entrepreneurs walk a delicate balance between the needs of their customers, teams and investors, and designers walk a delicate balance between their audience, colleague and founders.
Designers are uniquely suited to solving problems on multiple dimensions without losing sight of the ample opportunity to wow the customer – Yves Behar (Nast, 2021).
The Core Characteristics Of Entrepreneurship
Motivation – A design entrepreneur works long hours to get ventures off the ground and invest in everything to pursue a goal.
Passion – A design entrepreneur has a desire to make a difference and is passionate about the offering.
Vision – A design entrepreneur has a clear vision around goals, achievements and how to accomplish objectives to reach their goals.
Confidence – A design entrepreneur is confident in their abilities, services and offerings.
Emotional Intelligence & Communication Skills - Having a sustainable, profitable business means knowing how to work with people.
Decision Makers & Problem Solvers - A design entrepreneur has good decision-making skills and the capacity to make decisions quickly (5 Characteristics of an Entrepreneur | Vistage, 2021). They can view a problem from multiple dimensions without losing sight of the bigger picture.
Ethics Of Design Entrepreneurship
Design ethics are based on establish behaviours and actions accepted in the profession and a desire to help raise the standard for visual work and representation.
· Design professionals should strive to improve their professional, technical knowledge and skills through learning.
· Design professionals should continually seek to raise the standards of design aesthetics, function and innovation.
· Design professionals should seek to leave the world in a better place than they found it by contributing to society and the environment.
· Design professionals should contribute to and promote the profession through education.
Theory Of Entrepreneurship
The theory of entrepreneurship is centred around value creation. The whole entrepreneurial experience begins with intention, followed by discovering an opportunity and accumulation of the skills required to execute development and the appropriation of reward (Mishra and Zachary 2014).
The Transition From Designer To Entrepreneur
TheFutur's Jose Caballer and Chris Do are critical advocates for the transition and promotion of design entrepreneurship. This process begins by deciding on whether you are a designer or a design entrepreneur. Someone who is obsessive about their craft and wants to focus solely on design is at heart a designer. Much like an art director, a design entrepreneur has the skills to connect people, co-ordinate teams, share a conceptual framework, communicate and manage clients.
A design entrepreneur can seek out opportunities and recognise their unique value. They grow by realising their place in the value chain and operating differently to move up and become profitable. Learning is a critical element of the entrepreneurial journey. A designer needs to learn business, creative, technical, operational, sales and marketing skills. Being able to advocate or sell yourself is the final step on the road to design entrepreneurial success, alongside having the finances, networks and clients in place that allow them to take risks, pursue work they are passionate about and projects that make a difference (The Designer As Entrepreneur, 2014).
Many platforms are available to assists design entrepreneurs, such as TheFutur, Offscreen magazine (About Offscreen, 2021), Ethos magazine (About — Ethos, 2021), Backstage Talks (Read Backstage Talks Magazine, 2021), Creative lives in progress (About and Contact, 2021) and The Skool (The Designer As Entrepreneur, 2014).

Fig. 1: Issue 20, 2021.

Fig. 2: Milk Studio, 2021.

Fig. 3: Magazine, 2021.
With agencies shrinking and the technical revolution making design accessible to everyone, the market for employed designers is shrinking. More than ever, designers need to step out of their traditional roles and capitalise on inherent skills sets that make them highly suited for entrepreneurship. Designers need to be the founding teams that lead and drive the vision for entire companies and innovative products.
IMAGINE

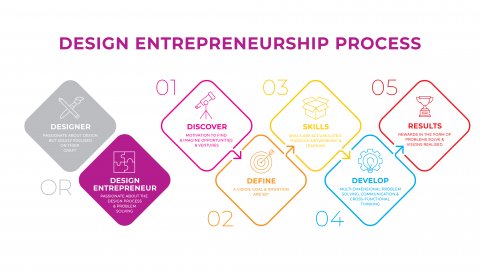
An infographic that highlights the practical definition and process of being a design entrepreneur.
Sketchbook Workshop Challenge Infographic Illustrating the Design Entrepreneurship Process.
The design entrepreneurship process begins by deciding on whether you are a designer or a design entrepreneur. Someone who is obsessive about their craft and wants to focus solely on design is at heart a designer who provides a service to a client. Design entrepreneurs are passionate about the process of designing and problem solving to develop a solution in a business venture with the skills to connect people, co-ordinate teams, share a conceptual framework, communicate and manage clients.
An entrepreneurial design process is comprised of five parts:
1) Discover
The motivation and ability to find opportunities and discover ventures others may have overlooked or not yet imagined.
2) Define
A clear vision around goals, achievements, intentions and how to accomplish these objectives is set.
3) Skills
To realise a vision or solve multi-dimensional problems, skills are accumulated through networking and learning. A designer needs to learn business, creative, technical, operational, sales and marketing skills to ensure success.
4) Develop
The accumulated skills allow for the development of multi-dimensional problem solving, confidently executed through
communication, decision making, team and client management, conceptual frameworks and cross-functional thinking.
5) Results
Rewards are a result of a problem being solved or the realisation of a vision.
REFLECTION
Design is a funny word. Some people think design means how it looks. But of course, if you dig deeper, it's really how it works – Steve Jobs. The process of how it works is a core design principle and what founding a company and entrepreneurship are all about (Pearson, 2021).
At its core, a design entrepreneur loves and is passionate about the process of designing and problem-solving.
Reference: Pearson, E., 2021. It Worked for Steve Jobs: Here's Why Spirituality is Critical for Entrepreneurial Success. [online] Entrepreneur. Available at: <https://www.entrepreneur.com/article/376117> [Accessed 1 August 2021].
Reference: Consultores, G., 2021. Five strategies that every startup should implement to sustain its business. [online] Entrepreneur. Available at: <https://www.entrepreneur.com/article/378479> [Accessed 1 August 2021].
Reference: Nast, C., 2021. Designers make great entrepreneurs; they just don't know it yet. [online] the WIRED UK. Available at: <https://www.wired.co.uk/article/designers-startups> [Accessed 1 August 2021].
Reference: Ethos-magazine.com. 2021. About — Ethos. [online] Available at: <https://ethos-magazine.com/about/> [Accessed 1 August 2021].
Reference: Creative Lives in Progress. 2021. About and Contact. [online] Available at: <https://www.creativelivesinprogress.com/information> [Accessed 1 August 2021].
Reference: Offscreenmag.com. 2021. About Offscreen. [online] Available at: <https://www.offscreenmag.com/about> [Accessed 1 August 2021].
Reference: Vistage Research Center. 2021. 5 Characteristics of an Entrepreneur | Vistage. [online] Available at: <https://www.vistage.com/research-center/business-leadership/20161027-5-characteristics-of-an-entrepreneur/> [Accessed 1 August 2021].
Reference: Designshack.net. 2021. What Are Design Ethics? (And Why Are They Important?). [online] Available at: <https://designshack.net/articles/business-articles/what-are-design-ethics-and-why-are-they-important/> [Accessed 1 August 2021].
Reference: Medium. 2021. What is design entrepreneurship?. [online] Available at: <https://medium.com/ma-communication-design/what-is-design-entrepreneurship-7d3f08ea33eb> [Accessed 1 August 2021].
Reference: Youtube.com. 2014. The Designer As Entrepreneur. [online] Available at: <https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nFm3uzNYQyU> [Accessed 1 August 2021].
Reference: Creative Lives in Progress. 2021. About and Contact. [online] Available at: <https://www.creativelivesinprogress.com/information> [Accessed 1 August 2021].
Reference: Backstage Talks Magazine. 2021. Read Backstage Talks Magazine. [online] Available at: <https://backstagetalks.com> [Accessed 1 August 2021].
Reference: Ethos-magazine.com. 2021. About — Ethos. [online] Available at: <https://ethos-magazine.com/about/> [Accessed 1 August 2021].
Image 1: Offscreen, 2021. Issue 20. [image] Available at: <https://www.offscreenmag.com/issues/20> [Accessed 1 August 2021].
Image 2: Milk Studio, 2021. Backstage Talks #1. [image] Available at: <https://www.behance.net/gallery/44002173/Backstage-Talks-1> [Accessed 1 August 2021].
Image 3: Magazine, E., 2021. Ethos Magazine. [image] Available at: <https://twitter.com/ethos_mag/status/841529467533164545> [Accessed 1 August 2021].